Quick Answer: The types of smart home sensors you need depend on your security goals, but most homes benefit from a mix of contact sensors, motion sensors, and environmental sensors. Together, these devices guard against intrusions, water damage, and fire hazards while offering real-time alerts and automation options for added peace of mind.
Keeping your home safe is no longer about clunky alarms or complicated wiring. The latest types of smart home sensors give you real-time protection that fits seamlessly into daily life.
From spotting water leaks before they cause thousands in damage to catching the sound of shattering glass, today’s sensors cover threats you may not have even considered.
If you are moving into a new apartment, upgrading your current setup, or building a DIY system from scratch, knowing which sensors truly matter – and how they work together – can make all the difference in creating reliable, affordable security.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Motion Sensors vs. Contact Sensors: The Foundation of Home Security
- Entry Sensors: Your First Line of Defense
- Glass Break Sensors: Protecting Your Windows Without Individual Sensors
- Motion Sensors: Covering Large Areas Efficiently
- Water Leak Sensors: Preventing Costly Water Damage
- Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Sensors: Life-Saving Detection
- Environmental Sensors: Temperature and Humidity Monitoring
- Building Your Sensor System: Integration and Priorities
- Want Peace of Mind for Your Home?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Sources
Key Takeaways
- Smart home sensors provide layered protection against intrusions, environmental threats, and fire risks, making them essential for modern home security.
- Motion sensors and contact sensors form the foundation, with each serving different roles in detecting movement and monitoring entry points.
- Entry sensors act as your first line of defense, covering front doors, garages, and hidden windows often overlooked by homeowners.
- Glass break sensors cover multiple windows at once, reducing costs while protecting rooms with large glass surfaces or historic designs.
- Motion sensors equipped with pet immunity minimize false alarms while offering wide-area coverage for stairways, hallways, and main living spaces.
- Water leak and environmental sensors prevent costly damage, with claims averaging over $11,000, and provide early alerts in hard-to-reach spaces.
- Batten makes it easy to choose tested and trusted smart sensors, offering bundles designed to give your home affordable, scalable protection.
Motion Sensors vs. Contact Sensors: The Foundation of Home Security
Motion sensors and contact sensors form the core of most home security systems, but they serve different roles. Knowing how each works, and where they perform best, allows you to design protection that detects true threats while minimizing false alarms.
Motion Sensors
- Scan entire rooms or zones using passive infrared (PIR) technology, which detects heat signatures from people moving through a space
- Cover large areas efficiently, with a single sensor often monitoring an entire living room or hallway
- Provide cost-effective protection compared to placing individual sensors on every entry point
- Particularly effective at catching intruders who bypass door or window sensors through unconventional entry routes
- Indicate that someone is inside your home but do not specify how they gained access
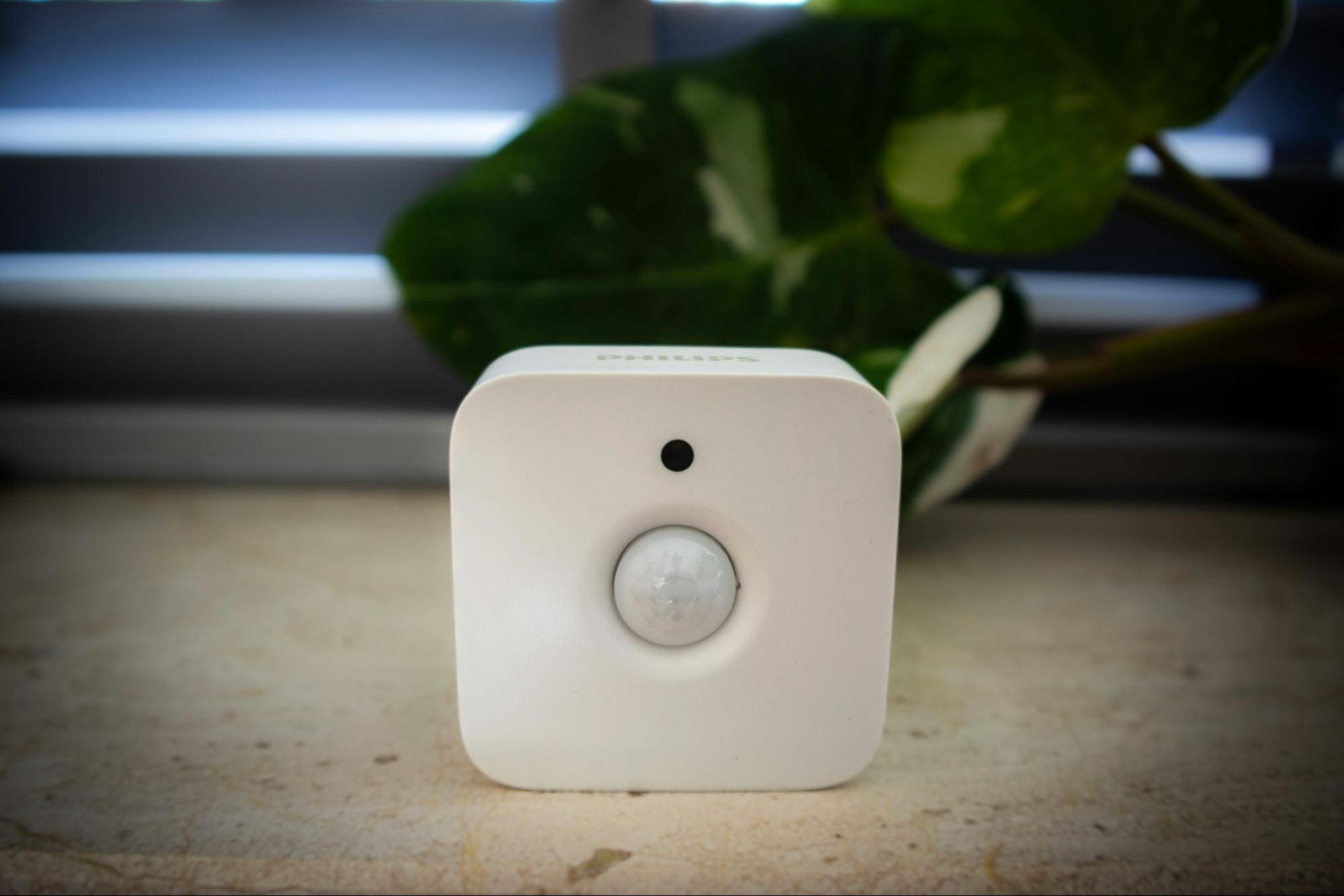

Contact Sensors
- Monitor specific entry points with two magnetic components that separate when a door or window opens
- Provide clear information about exactly which entry point has been breached
- Attach easily with adhesive strips, making them renter-friendly and simple to install without drilling
- Offer more reliability in homes with pets, since they do not trigger from animal movement
- Identify the exact method of entry, which is valuable for responding quickly and effectively
Choosing the Right Setup
The best choice often depends on your living situation and security needs. Renters usually prefer contact sensors for their ease of installation, while homeowners often benefit from combining both sensor types.
Families with pets frequently begin with contact sensors to prevent false alarms, then add motion sensors to cover interior spaces such as stairways or hallways.
For a practical approach, contact sensors on all ground-floor entry points paired with motion sensors in central areas create a layered system that balances precision and broad coverage – keep in mind that the right home security system can also significantly reduce insurance premiums.
Entry Sensors: Your First Line of Defense
Entry sensors are the gatekeepers of a home security system, monitoring doors, windows, and other access points. While early versions relied only on simple magnetic switches, modern entry sensors now include advanced features that make them smarter, more reliable, and better suited to today’s connected homes.
Key Features of Modern Entry Sensors
- Tamper detection that sends alerts if someone attempts to disable or remove the sensor
- Force detection that distinguishes between normal use and forced entry
- Smart lock integration to confirm whether a door was locked when opened
- Real-time status reporting to show if a door or window is open, closed, or left ajar
- Wireless connectivity for easy installation without complex wiring
Priority Placement Locations
Placing entry sensors requires considering how an intruder might approach a property. Many people secure only the front door but overlook less obvious vulnerabilities. Key locations include:
- Main entry doors (front, back, and side)
- Garage service doors and overhead garage doors
- Ground-floor windows, especially those hidden from view
- Sliding glass doors that can be lifted off their tracks
- Large pet doors that could allow entry
- Basement doors and windows
- Second-story windows accessible from trees, trellises, or low roofs
Maximizing Entry Sensor Effectiveness
For comprehensive protection, pairing contact sensors with smart locks provides valuable context by confirming not just when a door opens, but also whether it was secured. This is particularly helpful for families who want to ensure doors are locked after school or before bed.
Integration with other devices further increases security: lights can switch on when a door opens after dark, and cameras can automatically record anyone approaching. Garage door sensors also add peace of mind, sending alerts if the door remains open too long or operates unexpectedly while you are away.
Glass Break Sensors: Protecting Your Windows Without Individual Sensors
Glass break sensors provide an efficient way to secure multiple windows without installing a contact sensor on each one. They detect the acoustic signature of breaking glass, which includes both a low-frequency impact sound and a high-pitched shatter.
Why Glass Break Sensors Are Effective
- A single sensor typically covers a 15-25 foot radius, protecting several windows at once
- More cost-effective than attaching individual sensors to each window
- Ideal for large window arrays, sunrooms, or historic homes where contact sensors may not be suitable
Advances in Glass Break Technology
Early models were prone to false alarms triggered by loud noises like clattering dishes or television effects. Modern sensors now use dual-frequency detection and advanced algorithms, making them far more accurate at distinguishing actual break-ins from harmless household sounds.
Placement Tips
For best results, mount glass break sensors on walls or ceilings with an unobstructed line of sound to windows. Avoid placing them behind heavy furniture or in corners where acoustics are dampened.
They are most effective in large rooms with multiple windows. Pairing them with motion sensors adds another layer of protection, ensuring intruders who cut glass instead of shattering it are still detected once inside.
Motion Sensors: Covering Large Areas Efficiently
Motion sensors expand protection beyond entry points by monitoring entire rooms or passageways. They rely on passive infrared (PIR) technology to detect body heat and movement, making them a key part of layered home security.
Key Features of Modern Motion Sensors
- Pet immunity for animals up to 40-80 pounds, depending on the model
- Algorithms that distinguish human motion from pets based on heat size and movement pattern
- Advanced options that analyze behavior such as lingering or unusually slow movement
Placement Strategies
Position sensors at natural chokepoints like hallways, staircases, and main living areas. Mounting them 6-8 feet high in corners provides the widest coverage while minimizing blind spots. To reduce false triggers, avoid placing them near heat sources such as sunny windows, fireplaces, or HVAC vents.
Smart Capabilities
Newer motion sensors often integrate with connected systems, activating lights, adjusting thermostats, or triggering automated routines. Some models now include built-in cameras for visual verification, helping confirm whether an alert signals a real threat.
Water Leak Sensors: Preventing Costly Water Damage
Water damage is one of the most expensive and disruptive household issues, with average insurance claims exceeding $11,000. Smart water leak sensors provide early warnings before small leaks turn into major problems.
How Leak Sensors Work
Basic devices detect water by completing a circuit when liquid is present. More advanced versions use rope-style sensors to monitor long stretches such as basement perimeters or pipe runs. Many also include temperature sensors that warn of frozen pipe risks.
Best Placement Locations
Install leak sensors near water heaters, under sinks, behind toilets, beside washing machines, around sump pumps, and in basements or crawl spaces where leaks are more likely to go unnoticed.
Smart Features
Premium models can integrate with automatic shut-off valves, stopping leaks within seconds. This is especially valuable for vacation homes, rental properties, or any situation where water may flow for hours before being discovered.
Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Sensors: Life-Saving Detection
Smart smoke and carbon monoxide (CO) sensors improve on traditional alarms by providing faster, clearer, and more connected protection.
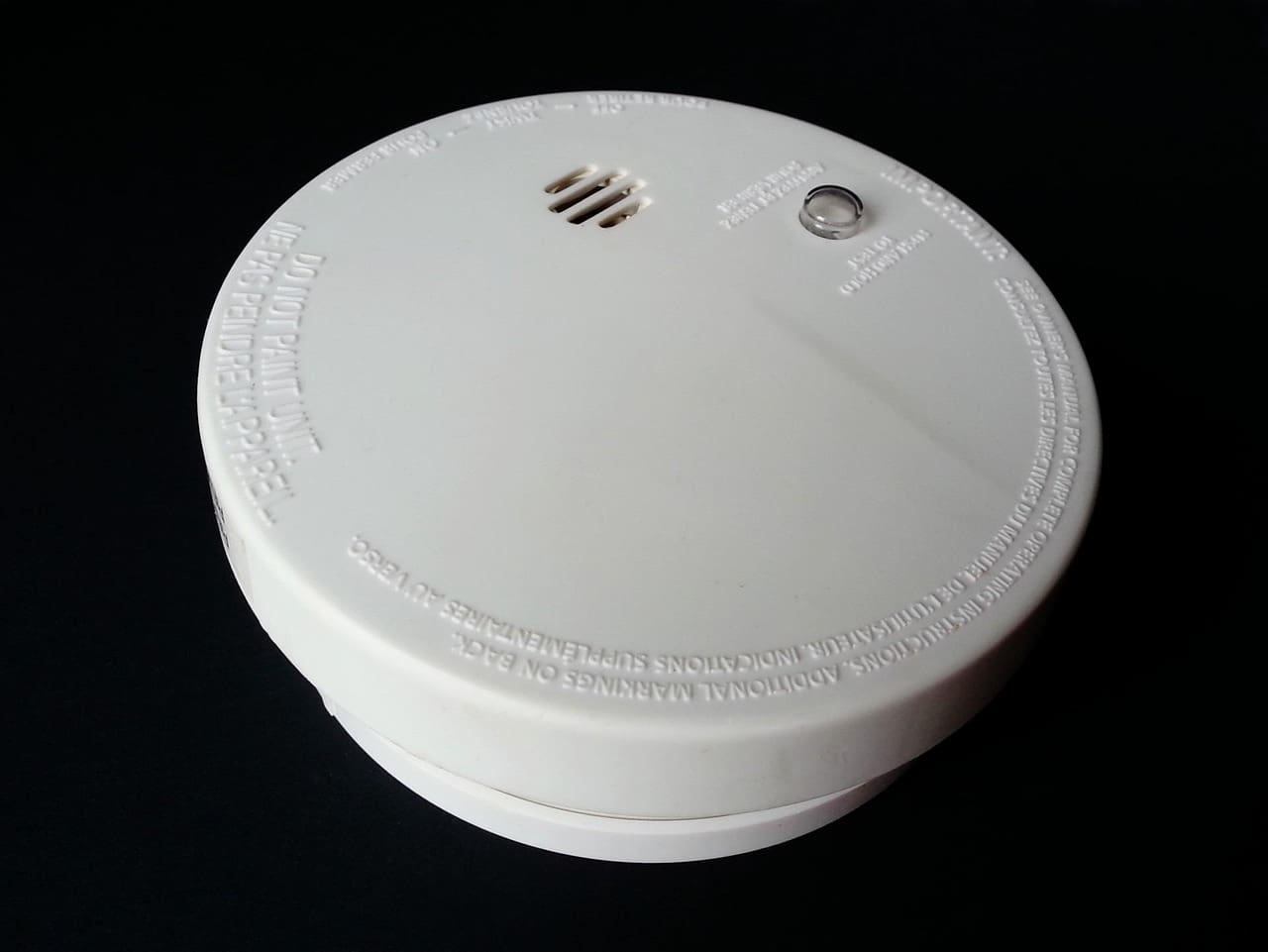

Why Smart Sensors Are Better
- Identify exactly which room triggered the alert
- Send mobile notifications, even when you are away
- Can integrate with smart systems to turn on lights during evacuation or shut off HVAC to limit smoke spread
Proper Sensor Placement
- Smoke Detectors: install in every bedroom, outside all sleeping areas, and on every level including attics and basements
- CO Detectors: place near all bedrooms and on each level that contains fuel-burning appliances or garages
Modern Features
Smart alarms often include voice alerts that specify the source of danger, distinguishing between small kitchen mishaps and real emergencies. Interconnected alarms ensure every device sounds if one detects a threat, which is vital in multi-level homes. Many systems also allow silencing through an app, reducing frustration from false alarms.
Data Point: Three out of five house fire deaths occurred in properties without working smoke alarms.
Environmental Sensors: Temperature and Humidity Monitoring
Environmental sensors address hidden risks that can cause costly damage over time. By monitoring temperature and humidity, these devices help prevent frozen pipes, mold growth, and structural issues that often go unnoticed until they become serious.
Temperature Monitoring Benefits
- Provides frozen pipe alerts in cold climates before ruptures occur
- Sends safety notifications for vulnerable residents such as older adults or pets during extreme heat or cold
- Detects rapid temperature spikes that may indicate fire risk
- Identifies HVAC malfunctions early, helping avoid expensive repair bills
Humidity Control Applications
- Reduces the risk of warped flooring, cracked furniture, or damaged cabinetry
- Protects sensitive items like electronics, wine collections, and musical instruments
- Works with smart systems to trigger dehumidifiers or fans automatically
- Helps prevent mold growth and discourages pests that thrive in damp conditions
Best Use Cases
Environmental sensors are especially valuable in areas you rarely monitor, such as attics, crawl spaces, basements, or vacation properties. When integrated into a broader smart home system, they allow HVAC adjustments based on whole-home conditions instead of relying on a single thermostat reading.
Building Your Sensor System: Integration and Priorities
Creating an effective sensor network requires balancing comprehensive coverage with practical constraints like budget, installation complexity, and your specific security concerns.
Start by mapping your home’s vulnerabilities – draw a simple floor plan and mark every potential entry point, valuable asset location, and area with environmental risks.
This visual approach helps identify coverage gaps and redundancies, ensuring you’re not over-protecting some areas while leaving others vulnerable.
Smart Sensor Comparison Chart
| Sensor Type | Coverage Area | Best For | Installation | Avg Cost | Battery Life |
| Contact Sensors | Single door/window | Renters, specific entry points | Easy (adhesive) | $15-40 | 3-5 years |
| Motion Sensors | 200-400 sq ft | Large areas, hallways | Moderate (mounting) | $30-60 | 2-3 years |
| Glass Break | 15-25 ft radius | Multiple windows | Easy (wall mount) | $40-80 | 3-5 years |
| Water Leak | Point or rope area | Basements, appliances | Easy (floor) | $20-50 | 2-3 years |
| Entry Sensors | Single entry point | All exterior doors | Easy (adhesive) | $20-40 | 3-5 years |
| Smoke/CO | Per room/area | Bedrooms, living areas | Moderate (ceiling) | $40-120 | 5-10 years |
| Environmental | Single room/zone | Storage, sensitive areas | Easy (shelf) | $30-70 | 1-2 years |
The effectiveness of your security setup depends heavily on how well your sensors work together. Integrated systems create layered protection by linking different devices into coordinated responses. For example, a door sensor can trigger a camera to start recording, activate lights, and send an instant alert to your phone. This kind of automated chain reaction offers stronger protection than isolated devices operating independently.
Benefits of Integration
Look for sensors that connect seamlessly with common smart home platforms or consider a unified system where every component is designed to work together. Integration not only strengthens security but also improves convenience.
Motion sensors can disarm automatically when you arrive home, or environmental controls can adjust based on occupancy, creating a system that adapts to daily routines.
Prioritizing on a Budget
When cost is a factor, it makes sense to prioritize based on the most likely threats and the potential damage they could cause.
- Entry Sensors on Main Doors: Most intrusions begin at doors, making these your first investment.
- Water Leak Sensors: Place near high-risk points like second-floor laundry machines, sump pumps, or older water heaters.
- Motion Sensors in Central Areas: A single sensor can cover multiple rooms or passageways.
- Glass Break Sensors: Add when you want to protect large or multiple windows without installing individual contact sensors.
Practical Approach
The best strategy is to begin with a core kit covering key entry points and high-risk areas, then expand as you learn how the system performs in real conditions. Even professional-grade installations often start small and grow over time.
For those weighing options, looking at alternatives to traditional camera systems – such as smart lighting, sirens, or automated alerts – can also help create a balanced, cost-effective security plan.
Installation Tips for Renters and DIY Enthusiasts
How you install your sensors depends on whether you are renting or setting up a permanent system in your own home. Renters need flexible, removable options, while DIY homeowners can commit to more integrated setups.
Renters
For renters, the challenge is adding security without breaking lease rules. Most smart sensors use strong adhesive strips, allowing you to mount them securely without drilling. Prepping the surface with rubbing alcohol helps them adhere properly but still come off clean when it’s time to move.
For heavier devices, use weight-rated command strips or removable mounting plates.
Cables can be tricky in rentals. Wireless sensors solve much of the issue, but anything requiring power needs neat routing.
- Adhesive Cable Channels: Paintable strips keep cords organized and unobtrusive.
- Flat Cords Under Rugs: Good for crossing open spaces safely.
- Hidden Power Strips: Place behind furniture for easy access.
Always take before-and-after photos to protect your deposit and simplify reinstallation.
DIY Homeowners
DIYers with more freedom can optimize placement and wiring.
- Recessed Door Sensors: Hidden inside frames for discreet protection.
- In-Wall Wiring: Eliminates battery swaps and keeps things tidy. If you’re already pulling wires, run extras for future devices.
- Outdoors, focus on Weather Resistance and Power Options: Solar panels can power standalone sheds, while hardwired sensors near existing outdoor lights provide the most reliable coverage.
With permanent installs, you can choose ideal heights and angles rather than working around adhesive limitations.
Smart Home Integration and Automation Possibilities

Once installed, smart sensors gain much more value when connected to your broader home automation system. Instead of acting only as alerts, they can trigger daily routines and emergency responses automatically.
Context-Aware Rules
Automation rules make sensors smarter. Motion at 2 PM might simply log activity, while motion at 3 AM could activate alarms, lights, and cameras. Door sensors can set personalized routines, such as turning on hallway lights or playing music depending on who is arriving.
Expanded Protection
It’s not just about intruders.
- Leak Sensors: Shut off water instantly when problems start.
- Smoke Alarms: Unlock doors and illuminate exit routes.
- Temperature Sensors: Activate attic fans before conditions become dangerous.
These preventative responses can stop small issues from becoming major emergencies.
Everyday Benefits
Beyond safety, smart sensors deliver peace of mind and convenience. They can help cut energy costs through motion-based lighting control, provide reassurance when kids get home, and detect early maintenance concerns. Integrated correctly, your system becomes proactive, protecting your home while simplifying daily life.
Want Peace of Mind for Your Home?
Smart home sensors have evolved into one of the most effective ways to protect your home, offering targeted coverage for doors, windows, hallways, and even hidden risks like leaks or carbon monoxide.
Motion and contact sensors form the foundation, while glass break and entry sensors provide precision at vulnerable points. Environmental and smoke/CO detectors add life-saving and damage-preventing protection.
By prioritizing sensors based on risk, starting with main entry doors and high-cost failure points, you can build a system that is both practical and scalable. When integrated into a connected ecosystem, these sensors go beyond simple alerts, triggering automated responses and simplifying daily routines.
With options suited for renters and homeowners alike, smart sensors provide flexible, affordable protection that adapts to your needs while ensuring your family and property stay safe.
Browse Batten Home Security’s expert-recommended sensor bundles and smart home security tools. From simple starter kits perfect for renters to comprehensive whole-home systems, find the right combination of sensors to protect what matters most. Our security experts have tested and vetted each product to ensure you’re getting reliable protection that’s genuinely simple to install and use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Smart Sensors Work Without WiFi or During Internet Outages?
Most smart sensors connect to a hub using protocols like Zigbee or Z-Wave rather than WiFi directly, meaning they’ll continue detecting and triggering local alarms even without internet.
That said, you’ll lose remote notifications and app control during outages. Some systems include cellular backup that maintains full functionality when your internet goes down.
For critical sensors like smoke detectors, we recommend models with both local alarms and smart features to ensure protection regardless of connectivity.
How Many Sensors Do I Actually Need for Basic Home Security?
A basic but effective setup typically includes contact sensors on all exterior doors (usually 2-3), motion sensors covering main living areas and hallways (2-3), and at least one glass break sensor for ground-floor windows.
This foundation costs around $200-400 and covers the most common intrusion routes. Water leak sensors near your water heater and washing machine add valuable protection against expensive damage for minimal additional cost.
Can Pets Trigger False Alarms With Motion Sensors?
Modern motion sensors with pet immunity can ignore animals under specific weight thresholds – typically 40-80 pounds depending on the model and settings.
These sensors analyze heat signature patterns and movement characteristics to distinguish between pets and humans.
Proper mounting height (6-8 feet) and angle adjustment further reduces false triggers. For homes with large dogs or multiple pets, contact sensors on doors and windows might provide more reliable primary detection.
What’s the Difference Between Professional and DIY Sensor Systems?
Professional systems typically include monitoring services, professional installation, and integrated equipment from a single manufacturer. DIY systems offer flexibility to mix and match sensors from different brands, no contracts, and self-monitoring options.
Professional systems often provide more reliable cellular backup and emergency response, while DIY systems cost less long-term and give you more control. Both can be equally effective when properly installed and maintained.
How Long Do Sensor Batteries Typically Last?
Battery life varies significantly by sensor type and usage. Contact sensors and glass break detectors often last 3-5 years since they use minimal power. Motion sensors typically need new batteries every 2-3 years due to their active scanning.
Smart smoke detectors can last 5-10 years with sealed lithium batteries. Environmental sensors that constantly monitor and report data might need annual battery replacement. Most systems send low-battery alerts weeks before failure.
Can I Install Sensors Without Drilling or Damaging Walls?
Absolutely – most modern sensors are designed for damage-free installation using industrial-strength adhesive strips. These mounting solutions hold securely for years but remove cleanly when needed. Command strips and similar products work well for heavier devices.
For the strongest hold without drilling, prepare surfaces with rubbing alcohol and ensure temperatures are above 50°F during installation. Many renters successfully secure entire homes without any permanent modifications.
Will Smart Sensors Work With My Existing Security System?
Compatibility depends on your current system’s technology and openness. Many traditional alarm systems can be upgraded with smart modules that add app control and smart sensor compatibility. Systems using standard protocols like Z-Wave often accept third-party sensors.
That said, some proprietary systems only work with their own sensors. Research your system’s compatibility before purchasing, or consider running parallel systems – keeping your traditional setup while adding independent smart sensors for enhanced features.




